The Future of Reality - Augmented, Virtual or Mixed?

Augmented Reality Provides Composite Views
Augmented reality (AR) is the integration of digital information with the user's environment in real time. Unlike virtual reality, which creates a totally artificial environment, augmented reality uses the existing environment and overlays new information on top of it.
One example of AR is the viral game, Pokemon Go, which greatly increased mainstream awareness of AR apps. The game uses AR to allow players to use their smartphone cameras to find Pokemon characters in a physical world by following a digital map.
A more recent example of the use of AR is with the Plane Finder AR app. Users can point their devices as a plane flies above and see data points like speed, destination, altitude and other detailed information.
2017 seems to be the year of AR - and has some very interesting statistics to boast about:
- Mobile AR could become the primary driver of a $108 billion VR/AR market by 2021 (Digi-Capital)
- Sales of AR smart glasses are expected to be worth $1.2 billion this year (CCS Insight)
- 60–70% of US consumers believe that AR can lead to workplace benefits, such as increased efficiency and better collaboration (ISACA)
According to PricewaterhouseCoopers, 24% of executives say they will make significant investments in AR over the next three years.
Engage in Different Worlds with Virtual Reality
Virtual reality (VR) allows users to experience a world that doesn't actually exist. The virtual world is created by devices that allows users to experience and interact with a 3D world that isn't real, by wearing a special headset or smart glasses and some form of input tracking. The display is typically split between the eyes, creating a stereoscopic 3D effect with stereo sound, and together with the technology and the input tracking, creates an immersive, believable experience, allowing users to explore the virtual world being generated by the device.
YouTube VR is one example of virtual reality that allows viewers to experience different situations. Using Google Cardboard or Google Daydream VR, users can be transported to the stage of the Broadway hit, Hamilton, or swim with sharks in the ocean.
Sports fans can feel as if they're on an NFL, NBA, FIFA, or NHL team through Oculus Rift's VR Sport Challenge. As a team member, players are immersed in the game and made to feel that they are on the field or ice rink, not just controlling a player as with regular 2D games.
Movies on some flights will also be enhanced with VR capabilities. Air France has a pilot program launched in 2017 where business class travellers will be able to watch 3D movies using VR headsets.
Here are some interesting statistics on VR:
- 171 million people will be users of Consumer Virtual Reality worldwide by 2018 (KZero)
- The installed base of virtual reality headsets is forecast to grow to 37 million by 2020 (Statista)
- The revenues from virtual reality hardware and software are projected to increase to over 40 billion U.S. dollars by 2020 (Statista)
Mixed Reality - Combining the Physical World with the Digital World
Mixed Reality (MR), also known as Hybrid Reality, aims to combine the best aspects of both virtual reality and augmented reality. It also refers to the entire spectrum of situations that span the continuum between virtual reality and actual reality. In this case, mixed reality can include augmented reality, augmented virtuality, and other mixed configurations.
Probably the most popular hardware for MR is Microsoft's Hololens. Described as "the first self-contained, holographic computer", it brings the physical & digital worlds together, allows users to engage with digital content and interact with holograms in mixed reality.
Racket: NX is a game that allow users to play a ball and racquet game in mixed reality. The futuristic arcade game can be played in single or multiplayer mode using the Oculus rift headset. It also features spatial audio technology for a truly immersive soundscape.
Here are some interesting statistics on MR:
- It is predicted that the video games segment will represent 34% of the augmented and MR software market in 2022 (Statista)
- The MR hardware market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 76.8% from 2016 to 2024 (Grand View Research)

For details on what AR, VR, MR mean - click here.
Augmented Reality - Past & Present
Today, most smartphones contain all the hardware required to be an AR device. However, head mounted, heads up (HUD), virtual retinal, and handheld displays as well as monitors optical projection systems, eyeglasses, and even contact lenses are being used for AR. IKEA's AR app, for example, allows customers to view products from the company catalog overlaid on a real-time image of a room viewed through a mobile device.
Augmented Reality Markup Language (ARML), a data standard to describe and interact with augmented reality scenes, is being used to standardize XML grammar for AR. Software is also being developed further to take advantage of hardware capabilities. Several software development kits (SDK) for AR are in development this year, including Vuforia, EasyAR, and Wikitude.
Aireal is a geospatial augmented reality (MR) platform that allows digital content to coexist with reality, creating infinite ways for people to experience their world like never before. Aireal's proprietary method of anchoring digital content at longitude, latitude, and altitude coordinates with millimeter precision provides shared experiential opportunities that are not limited by size or location. Aireal AR is visible through the use of mobile technology and is platform agnostic.
In addition to entertainment and games, AR apps are also being created for use in different industries, including art & architecture, construction, education, medical, and military.
Benefits of AR include:
- Relevant and helpful information in real time regardless of time or location
- Greater flexibility
- Improved efficiency
- Increased operational mobility
With developments continuing, there's no doubt that AR is growing. Developers are creating more AR experiences - and more importantly - more accessibility. As industry leaders continue to explore the possibilities of AR, we'll see a lot more applications in addition to what have already been recently introduced, like Snapchat's overlaying digital objects in the real world through its in-app camera. The possibilities of AR are limitless as it can be developed for many different uses. As companies like Microsoft, Google and Facebook have invested heavily in AR, today we're just seeing the tip of the iceberg of its capabilities.
The Current State of Virtual Reality
In April 2017, Facebook announced Facebook Spaces, a VR version of Facebook for the Oculus VR goggles. Users could create a custom avatar based on their Facebook profile and "hang out" with friends in a virtual space, such as a park, your living room, or any other space.
Microsoft's HoloLens is the first self-contained, holographic computer using a head-mounted display unit that enables users to interact with holograms. Some of the applications for the HoloLens include Microsoft's VR assistant, Cortana; a full-scale 3D modeling application, HoloStudio; and an augmented-reality first-person shooter game, RoboRaid.
A startup, Magic leap, is developing a head-mounted display that superimposes 3D computer-generated imagery over real world objects for applications in augmented reality and computer vision.
Samsung's Gear VR is the next generation Virtual Reality headset powered by Oculus. It transports users to new worlds through hundreds of games and millions of videos. A seated, interactive VR experience, the headset has a wide, 101-degree field of view and is compatible with Samsung Smartphones and major Samsung devices.
A full range of products and support from WorldViz includes enterprise grade software; complete VR systems including projection, standing, walking and seated VRs; custom solution design; and application development. WorldViz is described as "the world leader in innovative enterprise-level VR solutions and interactive visualizations," and has been delivering VR solutions and guidance in the field of science, business, and healthcare.
With the emergence of special headset and glasses, like the Sony PlayStation VR, Oculus Rift, HTC Vive, and Google Cardboard, there's no denying that VR today continues to move forward. Although VR is showing promise, it still has a long way to go before it can completely go mainstream. For one, VR needs to appeal not only to gamers, but to non-gamers as well. Furthermore, high prices continue to be an issue. Add the fact that not everyone has the graphical capabilities needed for VR, you can understand why it hasn't taken off as quickly expected.
Could MR be the Future of VR?
Microsoft just announced in 2017 that it will accept preorders on Mixed Reality Development Kits targeted at OEMs developing MR headsets. With numerous companies working on their own VR equipment, Microsoft is focusing on MR for the enterprise and consumer space to capture the market and be a leader in the MR space. Microsoft also believes that 'Mixed Reality' is the future, and is even implementing MR support for developers in the Creator's Update for Windows 10.
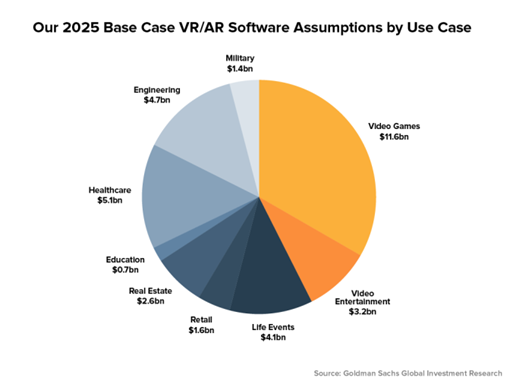
Goldman Sachs Research predicts that virtual and augmented reality will become an $80 billion market by 2025. Virtual reality, having improved since it was first launched, is not only used for fun and games, but is already changing the way industries are doing business. Mixed reality in the future will allow remote teams to collaborate to solve problems by interacting in real time.
In the healthcare industry, AR/VR is changing the way patients and doctors interact through virtual visits. Likewise, according to Goldman Sachs, AR/VR has the potential to aid doctors in everyday tasks and medical procedures, such as projecting CTI scans while operating, as well as having the potential to treat phobias and anxiety disorders.
Different types of learners will also benefit from MR, therefore, making it an ideal learning tool for the future. Visual learners will benefit from the immersion and optic stimuli of mixed reality. The reduction of noise that is present in open spaces and absent in MR will help listening, or auditory learners, and those who learn through physical activities, or kinesthetic learners, explore and collaborate in mixed reality. According to the National Education Center, there are over 50M K-12 students and over 20M College and University students in the US, making the potential user base for MR a large one.
MR will also impact the entertainment industry in the future. Multiplayer Broadcasting, which blends live TV with the interactivity of online games in a shared virtual world, is being looked into by the BBC's R&D UX team. As explorers of technology for the company's future, the British public service broadcaster believes it to be "the next iteration of audience participation shows in a broadcast-VR enabled future."
Use Cases with MR
Communication - MR will allow device users in different cities or countries to sit and interact with each other in the same space virtually across vast distances. It will have a major role to play in office communication and collaboration, but will also be a great tool for communicating with family and friends.
Education - Students will benefit and gain more comprehensive views and interactions using MR. Case Western University, for example, is using Microsoft's HoloLens to teach anatomy to its medical students. Students will be able to interact with objects in a 3D environment, learn about science and other subjects by being immersed in a virtual world or go on virtual field trips.
Entertainment - MR will enhance the way people play video games, and watch live events and video entertainment. Video game experiences will be heightened as AR technology transports both PC and console gamers into a virtual world. Sports fans can watch and interact with players, other fans, real-time game experiences and its advertisers and sponsors. Instead of watching movies the traditional way or even in 3D, viewers will be immersed in the movie. The only challenge is that movies will have to be filmed using a 360-degree camera - which will be costly.
Retail - The apparel and auto industries will benefit from MR as it can aid in high-end purchases. Volvo and Microsoft, for example, have partnered on a demo that will allow prospective car buyers to use HoloLens to digitally design cars at a dealership. Another use case is the ability for consumers to use VR/AR to see how clothes look without actually trying them on.
Military - Although already in use for several years, other use cases for military applications include flight and battle simulation and medic training.
Current Issues with Adoption
Real World Use Cases - One of the issues with the adoption is the need for more use cases for consumers to use MR. Some use cases have already included the communication, education and entertainment industries. However, MR can be used in a myriad of other industries. More use cases to show the importance of MR are needed in the fields of sports, music, healthcare, art and design, retail, construction, and real estate.
Connectivity & Network Performance: The maturity of technology also plays an important role in the adoption of MR. Faster performance of wireless networks is also needed for MR to be widely adopted. A slow connection, which is not ideal for transferring large amounts of data, will greatly affect the MR user experience. Until 5G networks are in place, we probably won't see MR being used by everyone just yet.
Content Formats: Optimization of content formats for MR is also crucial for adoption. This content has to have a target market. People need to find content useful - or at least interesting. One example is using a non-linear format such as the BBC's CAKE (Cook-Along Kitchen Experience), which customized video content adapted depending on different factors, such as viewer's dietary preferences and other information provided by the viewer.
Pricing: The key to mass adoption is by making Mixed Reality devices more affordable. MR devices have to be priced for the mainstream consumer base so it becomes accessible to more than just enterprise users. Hololens, for example, has a price tag of $3,000.00, which is not a price that will lead to mass adoption.
Consumer Adoption: To be a profitable industry, what drives the VR, AR, MR technology must not only be enterprise adoption, but broad consumer adoption as well. Broad consumer adoption will happen only when the price tags drop and there are more use cases and the need for consumers to buy them.
Fragmentation: Fragmentation, which is a main concern, exists in the industry because all the different platforms have their own formats and specifications. Right now, for example, there are headsets with different features that run on different platforms. It would be ideal if headsets would be able to run on multiple platforms.
Developer Ecosystem: There's a need for more developers to create content for consumers to use it. However, due to costs and standardization issues, developers are not creating content for the mass consumer in full force. This lack of content is what is holding VR back from becoming mainstream, so developers must create a variety of content that consumers will use.
Real Need: An important point for full-scale adoption is that VR has to be seen as a tool that is not merely for entertainment, but one that is a necessity.
Our Take - Will Reality Happen & when
VR, AR and MR are in the very early stages of development. Although widely associated with gaming, VR, AR and MR are believed to be the future of many businesses, particularly with the many uses cases already in place across industries. Improvements and enhancement will certainly push this technology further as it is integrated into our lives.
One way for "reality" to remain relevant is to find many more useful applications for the technology. For VR, AR and MR to really take off, it needs to become a necessity and an important part of everyday life. If "reality" can be implemented in a way that it improves productivity and task efficiency and not just for playing games or for enterprise use, then it will surely become mainstream much faster.
It is certain that these realities are not merely a passing trend as it has gained much attention in the past few years. As this technology continues to make waves in the technology field and with different companies creating their own version of gear and software, it is likely that this "reality" technology will become mainstream soon. Especially if adoption issues are resolved quickly, as we predicted last year, we see AR, VR and MR playing a bigger role in our lives by 2020–2025.